Colasoft Capsa are professional in monitoring and analyzing intranet packets and packets from internet, even packets crossing VLAN. Colasoft Capsa only need to be installed on the management machine, but other managed clients need not. Administrator needs to decide which machine to install Colasoft Capsa. Installation on different nodes, total captured packets number may differ. Therefore, you are recommended that you install or connect Colasoft Capsa to the central switch equipment, so that Colasoft Capsa will capture packets of your entire network to have a comprehensive monitoring and analysis. Of course you can use a TAP* to capture packets and analyze any network segment. Here we introduce you some common topology environments that Colasoft Capsa could have a sufficient monitor and analysis.
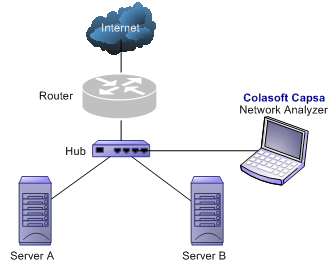
A shared network is also known as hubbed network which is connected with a hub.
Hubs are commonly used to connect segments of a LAN. When a packet arrives at one port, it is copied to the other ports so that all segments of the LAN can see all packets. A passive hub serves simply as a conduit for the data, enabling it to go from one device (or segment) to another. So-called intelligent hubs include additional features that enable an administrator to monitor the traffic passing through the hub and to configure each port in the hub. Intelligent hubs are also called manageable hubs. A third type of hub, called a switching hub, actually reads the destination address of each packet and then forwards the packet to the correct port.
With a shared environment, Colasoft Capsa can be installed on any host in LAN. The entire network data transmitted through the Hub will be captured, including the communication between any two hosts in LAN.

Switch is a network device working on the Data Link Layer of OSI. Switch can learn the physical addresses and save these addresses in its ARP table. When a packet is sent to switch, switch will check the packet's destination address from its ARP table and then send the packet to the corresponding port.
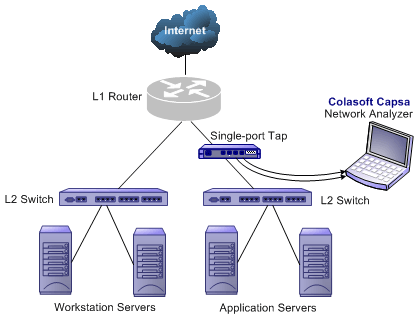
Generally all three-layer switches and partial two-layer switches have the ability of network management; the traffic going through other ports of the switch can be captured from the debugging port (mirror port/span port) on the core chip. To analyze the traffic going through all ports, Colasoft Capsa should be installed on this debugging port (mirror port/span port).
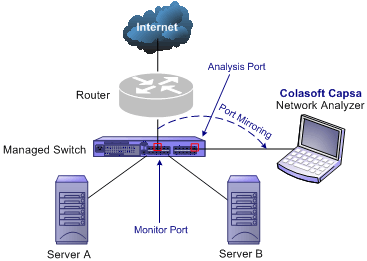
Some switches do not have the network management function. So there is no mirroring port as well. You can either, in this scenario, use a Hub or a TAP* to monitor and analyze your network with Colasoft Capsa.
TAPs can be flexibly placed on any line in network. When the requirement for network performance is very high, you can add a TAP* to connect your network.
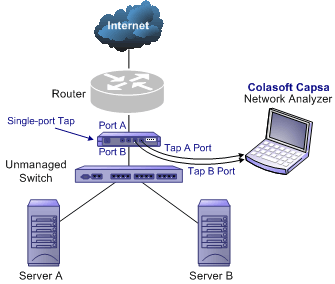
A Hub costs lower than a TAP* but lower performance than a TAP* in large traffic network.
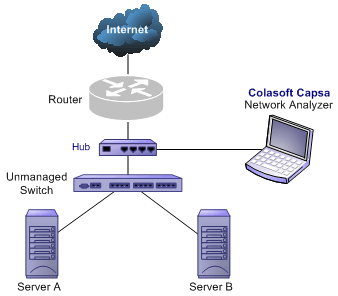
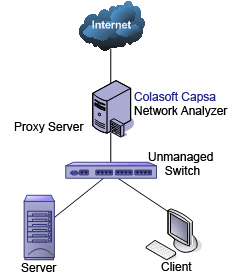
In the case when you only need to monitor the traffic in a network segment (e.g. Finance department, Sales department, etc.), you can connect the server on which Colasoft Capsa is installed and the network segment with an exchange facility. The exchange facility can be hub, switch or proxy server.
In small network, a proxy server is a reliable choice to deploy a network. Under this circumstance, you can install Colasoft Capsa directly on the proxy server.
Hub vs. TAP vs. Switch
| Hub | Switch (Mirror Port) | TAP* | |
| Positive |
Low cost No need configuration and settings No need to change original network topology |
No additional facility required No need to change original network topology |
No influence to network transmission performance No interference with data stream and raw data Does not occupy IP address, free from network attacks No need to change network topology |
|
Negative |
Additional facility (hub) required Interference to network transmission performance when meeting huge traffic Not applicable for big networks |
Occupies a switch port Possible influence to network transmission performance when meeting huge traffic. |
High cost Additional facility (TAP*) required Requires dual adapters Cannot connect Internet |
|
Comments |
A Hub works in a shared network and is common equipment used in early days of network deployment. It has been replaced by simple switches nowadays. A Hub is mostly used in a small network. |
A Management switch has port mirroring function which allows administrator to manage the network. Port mirroring is very applicable which mirrors 1 to 1 or 1 to all ports. Port mirroring is the most common management way at present. |
A TAP* is very applicable to be installed at any place of a network. Under large traffic, a TAP* should be a reasonable choice if its high cost is ignored. |
 Ways of configuring port mirroring would be different from different switches or models. See Switch and Port Mirroring to learn common-used switch port mirroring configurations.
Ways of configuring port mirroring would be different from different switches or models. See Switch and Port Mirroring to learn common-used switch port mirroring configurations.
![]() * TAP is not supported by the Free version.
* TAP is not supported by the Free version.
|
Back |
| Copyright © 2001 - 2010 Colasoft. All rights reserved. |