How to Locate the Source of Packet Loss with Network Analyzer
Packet loss is usually difficult to troubleshoot, because there are many possible causes for that. It always takes a long time to troubleshoot such issues. In this case, we use Capsa network analyzer the source of packet loss by packet analysis and comparison.
Problem Description
Most of hosts which are under DoS attack will show high CPU and memory usage or network bandwidth is occupied by garbage traffic.Programmable logic controller (PLC) is a type of programmable memory, which performs user-oriented instructions such as logical operations, sequential control, timing, counting, and arithmetic operations. Besides, it controls various types of machinery or production processes through digital or analog input/output. PLC is a kind of computer specially used for industrial control.
A PLC equipment of a company has been abnormal recently that the equipment often reports connection failure. The IT team found there is packets loss of the PLC by Ping test, and the packets loss rate is 1-2% around. To find the causes, and avoid similar problems in the future, the company turned to Colasoft. With the assistance of Colasoft network analysis expert, Capsa network analyzer was by-pass deployed at the access switch which connect to the abnormal PLC to perform packet analysis.
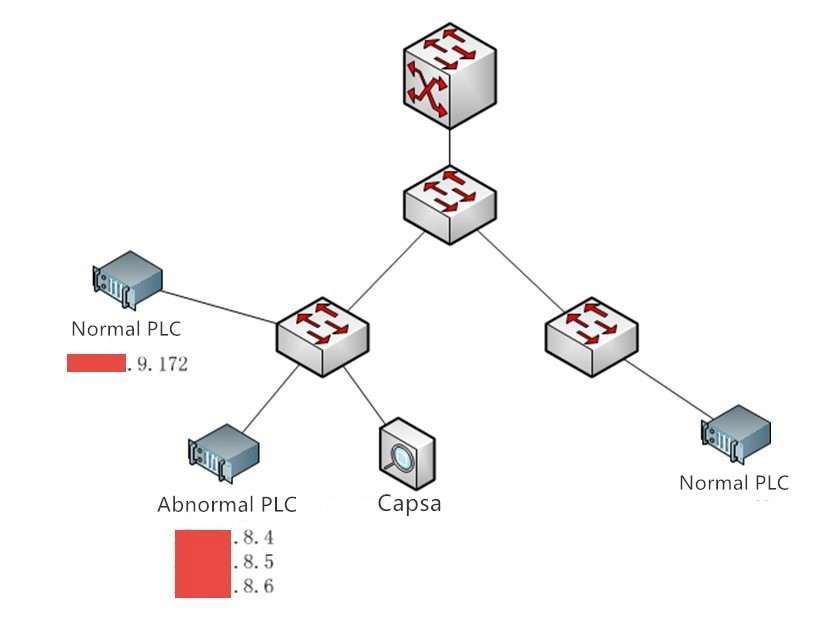
PLC network environment and deployment
Analysis
We analyzed the conversations of abnormal PLC NICs and normal PLC NICs respectively for comparison.
Analyze packets for single NIC of abnormal PLC
Mirrored the bi-directional traffic of the NIC (IP XX.XX.8.4) of the abnormal PLC. At the same time, the technology engineer pinged XX.XX.8.4 from the core switch. From the captured ICMP packets, we can find that there are 124 ping req packets captured during the test. But there were only 122 ping Reply packets captured.
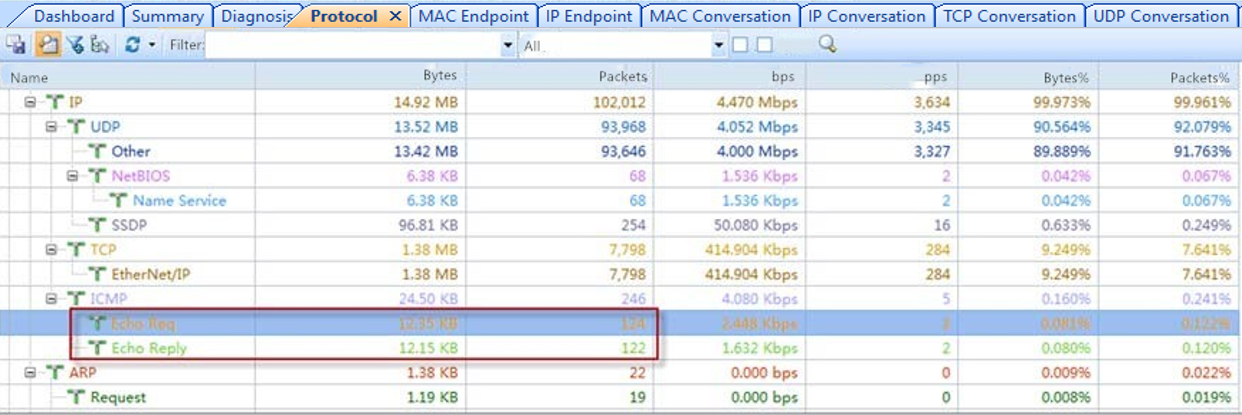
From the screenshot above, packets loss occurred from the abnormal PLC to the interface of the edge switch, and 1.6% of the packets were not transmitted to the edge switch. At the same time, there was packets loss in XX.XX.8.4 TCP conversations.
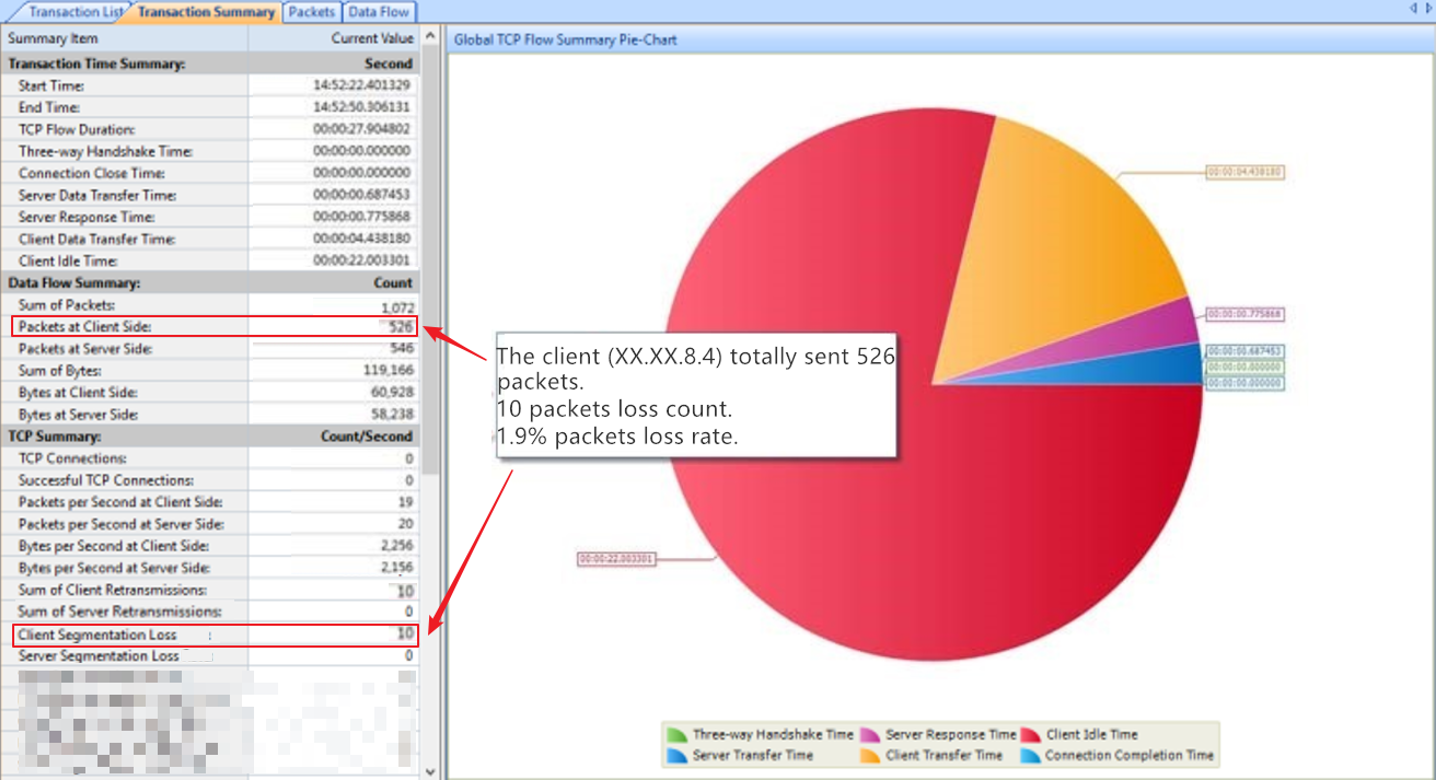
Based on the information above, we can preliminarily determine that the causes for packets loss is between the abnormal PLC and the switch. There are multiple possible causes, the abnormal interface accessing to switch, the abnormal Ethernet cable, the abnormal PLC’s NIC or other abnormal hardware.
Analyze packets for all NICs of abnormal PLC
Mirrored the bidirectional traffic of all the NICs of the abnormal PLC and we found packets loss in all three NICs.
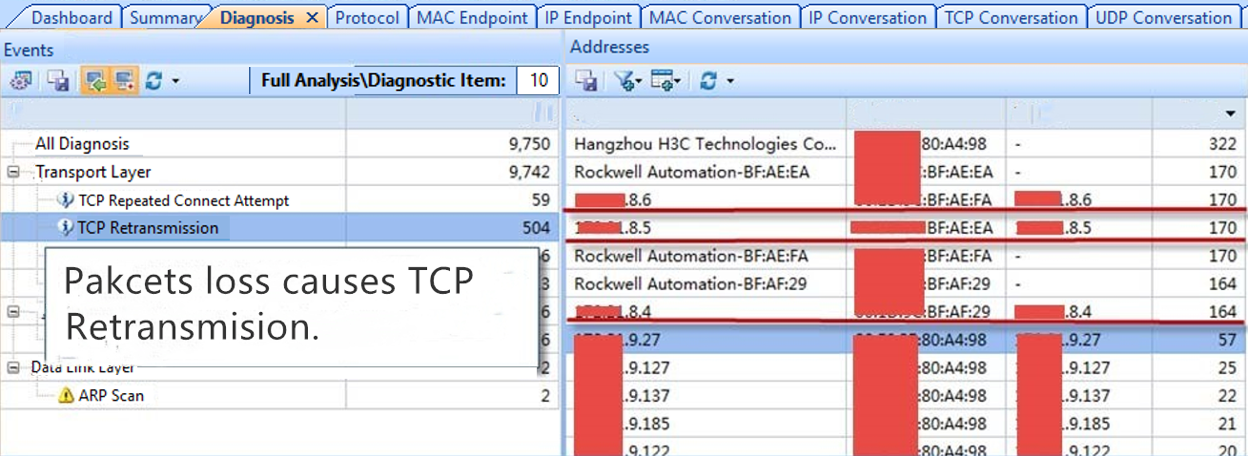
It shows that the causes for packets loss is not only from the NIC XX.XX.8.4, but from the three network NICs of the abnormal PLC. According its TCP conversations statistics, it was proved that packets loss occurred when data was sent from the PLC to the access switch.
Since it is almost impossible for three network cables or three switch interfaces to have problems at the same time, we can basically determine that the problem was caused by the abnormal PLC.
Analyze packets for normal PLC
Mirrored the bidirectional traffic of the NIC (IP XX.XX.9.172) of the normal PLC. From the information, we can find out that there are a few TCP retransmissions, which is due to the conversations related XX.XX.8.4.

It indicated that there was no packets loss between the normal PLC and the access switch, and further verify the previous analysis result.
Analysis Conclusion
Based on the packet analysis above, the pack loss problem is most likely caused by the hardware of the PLC, which leads to packets not being sent from the NIC to the network. It is unlikely that network cable or access switch port will cause packet loss.
Value
By packet analysis in depth, IT team can quickly locate problems from multiple possible causes, so that packet loss will not be a problem for the IT team anymore.